Medical activities
HIV/AIDS
Without treatment, half of infected children die before their second birthday.
At the end of 2017, approximately 36.9 million people were living with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), most of them in sub-Saharan Africa. Although there is currently no known cure for HIV/AIDS, a combination of the two, known as antiretroviral therapy (ARV), allows patients to live longer and healthier lives.
The HIV virus is transmitted through blood and body fluids and gradually weakens the immune system – usually over a period of three to ten years, leading to acquired immune deficiency syndrome – AIDS. As the immune system weakens, a number of other infections can develop. The most common of them is tuberculosis, which often leads to death.
The cost of medicine is now cheaper than ever before. But it is still necessary to make efforts for quality treatment, which will allow the infected to live a longer and healthier life.
MAGNA has been providing care to patients living with HIV/AIDS since 2002. We were one of the first to start giving life-saving ARV treatment to pediatric patients in Cambodia. Subsequently, we expanded our HIV/AIDS programs to Vietnam, Kenya, Haiti and Nicaragua.
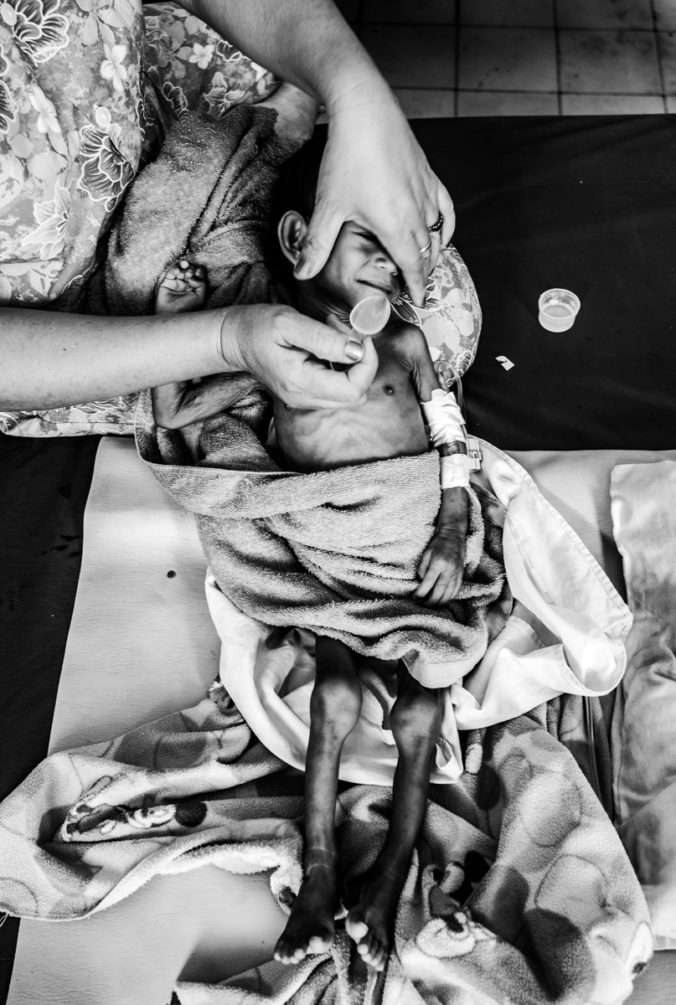
More than 90% of children living with HIV acquired the infection from their mothers.
A simple blood test can confirm the presence of HIV, yet many people live for years without symptoms and never know they have been infected. Around 30% of people worldwide are currently infected with HIV but are unaware of it. If the patient is diagnosed with this disease, monitoring of the viral load and measurement of the level of the HIV virus in the blood is necessary to ensure a functioning and effective treatment. While viral load tests are routine in rich countries, access to them still lags in developing countries.
Treatment
A combination of drugs known as antiretrovirals (ARVs) help fight the virus, reduce the spread of infection, and allow patients to live longer, healthier lives without rapidly deteriorating immune systems. Children living with AIDS are one of the greatest tragedies and challenges in the fight to control this disease. WHO estimated that in 2006, 2.5 million children under the age of 15 were living with HIV/AIDS, with an additional 1,200 children being infected each day. Without treatment, half of these children die before their second birthday.
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT)
More than 90% of children living with HIV acquired the virus from their mothers during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) can reduce the chance of transmission to less than two percent. MAGNA integrates PMTCT into maternal and child care, which includes testing and provision of antiretroviral drugs (ARVs) to HIV-positive pregnant women, breastfeeding counseling and preventive ARV administration to newborns.
Psychosocial support
Mental health care is an integral part of MAGNA’s HIV/AIDS treatment programs. All patients receiving ARV treatment at MAGNA clinics and hospitals have access to psychosocial support.
More about HIV/AIDS in our projects
Learn more about how we help victims with HIV/AIDS in our projects worldwide
